Summary
Geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and fluctuating energy prices are driving up fertilizer costs worldwide. This article explores the current market dynamics, their impact on agriculture, and the potential consequences for farmers and food production.
Factors Influencing Fertilizer Prices
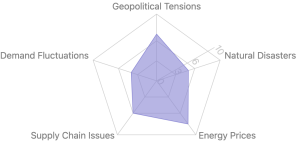
The global agricultural sector is facing a significant challenge as fertilizer prices continue to rise. Several factors are contributing to this trend:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Instability in the Middle East is affecting production and export of fertilizers from key producing countries.
- Natural Disasters: The Atlantic hurricane season, particularly Hurricanes Helene and Milton, has disrupted production and transport infrastructure in the US Gulf region.
- Energy Prices: Elevated crude oil and natural gas prices are increasing production costs, especially for nitrogen-based fertilizers.
Market Dynamics and Price Trends
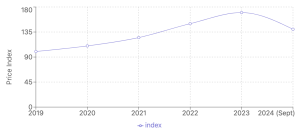
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), fertilizer supplies were tight in September 2024, with phosphate fertilizers being particularly scarce. All fertilizer cost indices remained significantly above their 2019 baseline levels, although they have improved compared to September 2023.
Recent data shows:
- CBOT-listed third-month futures contracts for Middle East and US Gulf granular urea increased by 6.4% and 5.1% respectively in early October.
- Natural gas prices increased in the US due to supply disruptions, while European prices eased due to sufficient inventories.
- Ammonia prices increased despite subdued demand, driven by tight availability.
Regional Impacts and Export Concerns
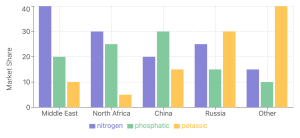
Several Middle East and North African (MENA) countries play crucial roles in the global fertilizer market:
- Oman, Egypt, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia are major exporters of nitrogen-based fertilizers.
- Egypt and Israel are significant exporters of phosphatic fertilizers.
- Jordan is an important exporter of potassic fertilizers.
China's continued export restrictions are keeping supply tight, particularly as demand in Brazil and Europe is expected to increase.
Implications for Farmers and Agriculture
The rising fertilizer prices pose significant risks to agriculture:
- Increased Production Costs: Farmers may face higher input costs, potentially affecting their profitability.
- Demand for Higher Crop Prices: To offset increased costs, farmers might seek higher prices for their produce.
- Potential Shifts in Crop Choices: Some farmers may adjust their planting decisions based on fertilizer requirements and costs.
- Food Security Concerns: Higher fertilizer prices could impact food production and potentially lead to increased food prices.
Conclusion
The current trend of rising fertilizer prices presents a complex challenge for the global agricultural sector. While the situation has improved somewhat since 2023, prices remain significantly above historical baselines. Farmers, policymakers, and agricultural businesses must stay informed about these market dynamics and consider strategies to mitigate the impact of high fertilizer costs. As we move forward, monitoring geopolitical situations, energy markets, and weather patterns will be crucial for understanding and navigating the fertilizer market. The agricultural sector may need to explore alternative fertilization methods, improve efficiency in fertilizer use, or consider crop diversification to adapt to this evolving landscape.