Summary:
India's recent removal of export restrictions on rice, combined with Vietnam's agricultural challenges and Pakistan's limited stocks, is creating significant shifts in the global rice trade landscape. This comprehensive analysis explores how these changes are affecting prices, market dynamics, and future outlook for rice trading, while examining the broader implications for global food security and trade patterns.
Market Developments
The global rice market is experiencing a transformative phase following India's decision to fully remove export restrictions. This policy shift has immediate implications for global pricing and trade dynamics, creating ripple effects across Asian and African markets.
Price Pressure and Market Response
- Current prices have dropped below $575 per tonne for most varieties
- Excluding premium categories like fragrant, long-grained, and basmati rice
- Pakistan leading with most competitive pricing at $481-485/tonne for 5% broken white rice
- India now offering at $488-492/tonne
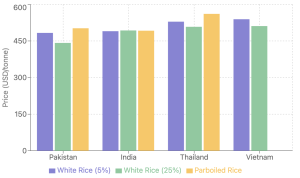
Competitive Landscape Analysis
1. Current 5% Broken White Rice Prices:
- Pakistan: $481-485/tonne
- India: $488-492/tonne
- Thailand: $529/tonne
- Vietnam: $537-541/tonne
2. 25% Broken White Rice Prices:
- Pakistan: $440-444/tonne
- India: $491-495/tonne
- Thailand: $508/tonne
- Vietnam: $509-513/tonne
3. Parboiled Rice Market:
- Thailand (100% sortexed): $561/tonne
- Pakistan: $500-504/tonne
- India: $490-494/tonne
Regional Dynamics and Market Implications
Vietnam's Structural Challenges
- Agricultural growth slowdown in first nine months of 2024
- Severe impact of Typhoon Yagi on crop cultivation
- Declining rice production area due to:
- Strategic shift to other farming activities
- Accelerating urbanization
- Climate change effects
- Feed ingredient import strategy:
- Increased imports of corn and wheat
- Focus on diversifying supply sources
- Adaptation to lower global grain prices
India's Strengthening Market Position
Policy Changes
- Complete removal of $490/tonne minimum export price for white rice
- Elimination of 10% duty on parboiled rice
- Strategic positioning in global markets
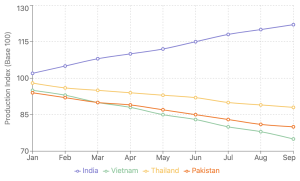
Production Advantages
- Abundant stocks in key states like Haryana and Punjab
- Digital crop survey revealing additional 65 lakh hectares under paddy
- Potential production increase of 10 million tonnes
- Strong domestic procurement program
Infrastructure Support
- Well-maintained buffer stocks
- Efficient distribution network
- Modern storage facilities
- Strategic port locations for exports
Supply Chain Implications
Logistics Considerations
- Port Congestion:
- Reduced waiting times at Indian ports
- Improved loading efficiency
- Better container availability
- Transportation Networks:
- Enhanced rail connectivity to ports
- Improved inland transportation
- Strategic storage locations
- Quality Control:
- Stricter quality parameters
- Enhanced testing facilities
- Better preservation techniques
Impact on Global Trade Flows
Short-term Effects
- Immediate price adjustments in key markets
- Changing buyer preferences
- Shift in traditional trade routes
Long-term Implications
- Evolution of trading partnerships
- Development of new market channels
- Changing dynamics in price discovery
Market Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities
- For Traders:
- Arbitrage possibilities between markets
- New origin-destination pairs
- Enhanced price competitiveness
- For Importers:
- Better price discovery
- Multiple sourcing options
- Improved quality-price ratios
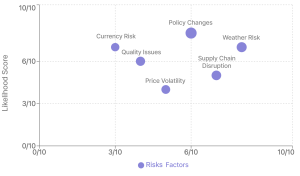
Risk Factors
- Weather-related Risks:
- Monsoon dependence
- Climate change impact
- Natural disasters
- Political Risks:
- Policy changes in exporting countries
- Import regulations
- Trade barriers
Future Outlook
The market is poised for continued evolution due to several factors:
- India's substantial buffer stocks and production capabilities
- Favourable soil moisture conditions supporting cultivation
- Good water reservoir levels ensuring irrigation support
- Potential for strong rabi paddy production
- Changing global demand patterns
- Evolution of consumption preferences
Technology and Innovation
- Digital crop monitoring systems
- AI-powered yield prediction
- Blockchain in supply chain tracking
- Smart contract implementation
Conclusion:
The global rice market is entering a new phase with India's policy liberalization leading the way. The combination of increased production capabilities, competitive pricing, and technological advancements suggests a more efficient and transparent trading environment. Traders and importers should closely monitor India's rabi paddy output, Vietnam's recovery from weather-related challenges, and emerging technological solutions to make informed trading decisions. The market dynamics indicate increased competition among exporting nations, potentially benefiting buyers while necessitating more sophisticated risk management and trading strategies.
